Power supply modules for demanding energy solutions
In an increasingly digital world, excellence in electricity supply is already determining winners and losers.
We know that a high-quality and reliable supply of electricity is a prerequisite for the continuous operation of the information infrastructure and support systems in the data center. However, the availability of electricity supply does not only mean reducing the risks of longer power outages. Even more frequent are short-term outages and phenomena of overvoltage and reduced voltage.
But what about when the capacity of the information infrastructure increases, when the requirements for additional support systems also increase and the need for electrical energy jumps? In the data center, only 30% of the total electricity is used for the operation of the information infrastructure!
What should your new power system do?
Uncompromising availability
With a combination of continuous and uninterruptible power solutions, we offer TIER III or TIER IV availability!
Fast connection of the tested system
Power modules for demanding energy solutions are built and pre-tested by NTR and ensure almost immediate connection upon delivery to your location.
Scalability and flexibility
The design of the NTR power modules allows you to either add power sources and support equipment or assemble multiple power modules. In this way, your power supply system grows easily with increasing consumption, without the need for oversizing.
Highly available systems of power supply NTR RPS™
The following types of power supply are recognized in hierarchical systems of power supply:
- Network supply, sometimes called the general own consumption. It is a power supply network that supplies ordinary users on the network with power. The quality of electrical energy and the parameters of reliability are specified in the QoS specification of the operator or distributor of electrical energy. In general, the acceptable total yearly duration of unplanned interruptions longer than 3 min should not exceed 400 minutes. The highest acceptable number of these interruptions is 10. Force majeure and outside reasons are excluded from the total duration. Additionally it is acceptable to have up to 22 unplanned interruptions shorter than 3 minutes.
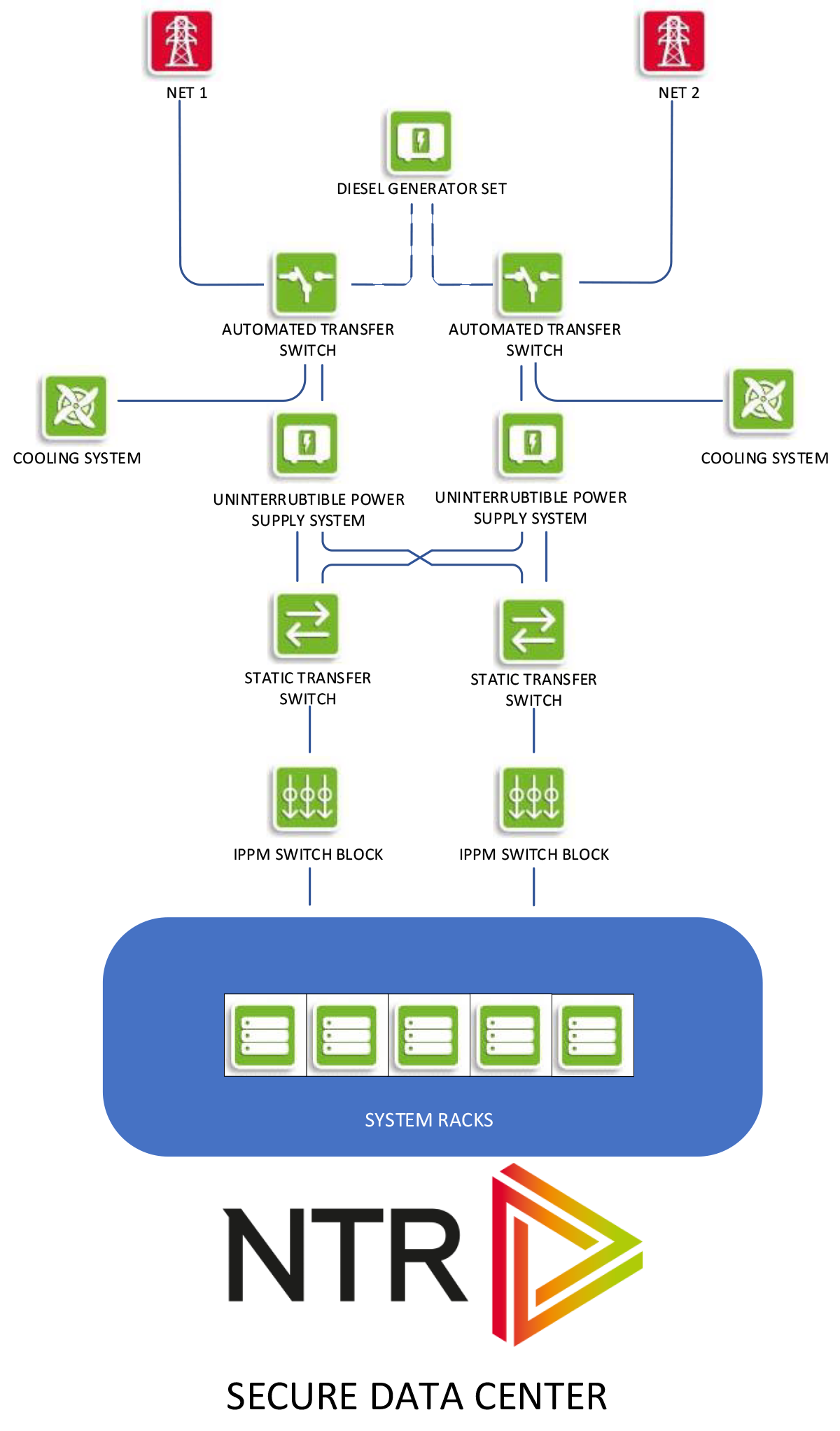
- Backup power supply, sometimes also called urgent own use. It is a power supply network, that supplies consumers who have to work even during protracted electrical energy outages (over 2-3 minutes), planned as well as unplanned. Electrical power in these networks is ensured by the normal operation of the network and in case of loss thereof from spare resources. The characteristic of spare resources is that they need a relatively short period of time to provide consumers with electrical energy. A typical example of a reserve source is a diesel electric power plant (hereinafter referred to as DEA). Examples of consumers which must be supplied from the emergency power supply are cooling systems in demanding technical installations, security systems, pumps, joint equipment in power plants, objects of special interest such as hospitals, elevators in high-rise buildings...
- Uninterruptible power supply, generally called UPS. It is a power supply network that supplies customers that must be continuously supplied with electrical energy. Typical users are fire protection systems, anti-theft systems in high security facilities, various computer and information systems, telecommunication systems and the like. Normally UPS systems in these networks serve as an energy source supplied by the network or backup power supply, and in case of interruption can supply energy from emergency sources such as batteries or accumulators.
- Uninterrupted Power Supply is a denomination that is not yet widely recognized and used. Selected because of the specific problems of users, to whom the availability of uninterrupted power supply is not sufficient and also need more reliable sources. Increased reliability in the devices themselves above a certain rate can no longer be achieved; therefore it is necessary to resort to parallel connection of different systems. To avoid the problem of syncing sources in different networks (UPS or generator), static transfer switches are arranged, that provide switching between sources within of time allowed (see diagram ITIC).
Classification and arrangement of the systems according to the tier standard
The American organization Uptime Institute first started defining the recommendations or guides for the regulation of ICT infrastructure according to their required availability. As part of the recommendations are basic guidelines of how to ensure an appropriate utility infrastructure according to the required or desired availability. According to the latter, utility infrastructures of data centres are arranged in four categories in accordance with the following table:
|
Category I |
Category II |
Category III |
Category IV |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Redundancy of software |
N |
N+1 |
N+1 |
2x(N+1) |
|
Power supply route |
1 |
1 |
1 active 1 passive |
2 |
|
Maintenance during operation |
Not required |
Not required |
Yes |
Yes |
|
»Single point of failure« |
In several locations |
In several locations |
In some places |
Without |
|
Tolerance to outages |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Multiple fire protection zones |
Not required |
Not required |
Required |
Required |
|
The load on the area |
220 – 230 W/m2 |
Up to 450 W/m2 |
Up to 1620 W/m2 |
Above 1620 W/m2 |
|
Limitation of operation due to maintenance |
2 shutdowns longer than 12 h/year |
3 shutdowns longer than 12 h/2years |
No shutdowns |
No shutdowns |
|
»Downtime« |
1,2 outages longer than 4 h/year |
2 outages longer than 4 h/2years |
2 outages longer than 4 h/5years |
1 outage longer than 4 h/5years |
|
The total annual DT |
Up to 28 h |
Up to 22 h |
Up to 1,6 h |
Up to 0,8 h |
|
Availability |
Up to 99.671% |
Up to 99.749% |
Up to 99.982% |
Up to 99.991% |
Elements of uninterrupted power supply systems
Uninterruptible networks are, like any other energy network, composed of basic elements. These are, in addition to the conductors themselves, other components responsible for ensuring energy supply, its production, distribution and monitoring or control. In general, we can say that elements of the UPS network can be divided into the following groups:
Elements for switching and distribution of electric energy, which include:
- switchboards,
automatic transfer switches,
static transfer switches,
PDU units (power distribution units),
power cables and cabling installation,
grounding system.
Components for production and delivery of electric energy, which include:
- various generators,
- various uninterruptible power supply systems.
Elements such as energy sources in uninterruptible power supply systems, which primarily include:
- rechargeable batteries,
- fuel cells,
- kinetic energy reservoirs,
- other sources of energy.


